SuperSites
Gingin Banksia Woodland SuperSite
TERN’s Gingin Banksia Woodland SuperSite is on the Swan Coastal Plain, approximately 10 km southwest of Gingin and 80km north of Perth, Western Australia. The site sits in a natural woodland of high species diversity (overstorey dominated by Banksia spp) that overlays the Gnangara groundwater mound, Perth’s most important groundwater resource. The site is 2 km from the University of Western Australia International Gravity Wave Observatory. The traditional owners at Gingin are the Yued group of the Noongar People.
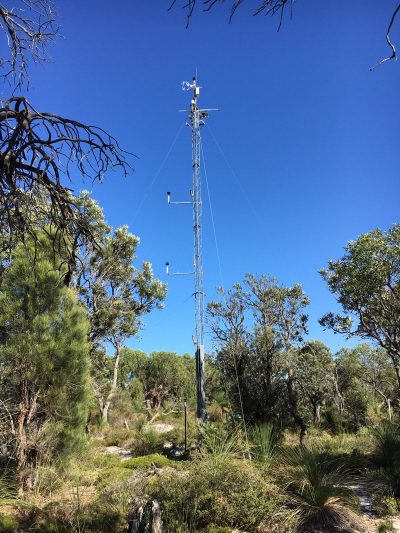

Site Infrastructure & Characteristics
SuperSite Research Infrastructure
- One eddy-covariance flux tower – measurements at 7m and 15m
- Soil water content and temperature sensors
- 2 1 ha Surveillance monitoring plots
- COSMOS soil moisture sensor
- Groundwater monitoring bores

SuperSite Details
- Vegetation type: Coastal heath banksia woodland
- Elevation: ~51 m
- Rainfall: ~681 mm/yr
- Mean Temperature: ~18.4°C
- Soils: Podosol sands
Site Research
Research using the Gingin Banksia Woodland SuperSite aims to increase our understanding of how climate, water and vegetation are interacting. Research is quantifying groundwater recharge and surface–atmosphere exchanges of carbon-dioxide, water vapour and energy at the Gingin site and analysing the ecological and social consequences.
The Gingin SuperSite is collocated with the Land Ecosystem Atmosphere Program (LEAP) – Gingin.
Featured Dataset
This dataset consists of measurements of the exchange of energy and mass between the surface and the atmospheric boundary-layer in Banksia woodland on the Swan Coastal Plain 70km north of Perth, Western Australia using eddy covariance techniques.
More Datasets
Site Partners




Research Publications
Since its inception, TERN’s infrastructure has enabled the publication of more than 1600 peer-reviewed scientific journal articles or books.






